Consumer Mapping involves understanding and visualizing the journey a customer takes with a brand, from awareness to post-purchase interactions. This process helps businesses gain insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and pain points. The key components of consumer mapping include:
- Customer Personas: Detailed profiles of target customers, including demographics, psychographics, behavior, motivations, and goals.
- Touchpoints: Points of interaction between the customer and the brand, such as social media, website visits, email communication, and in-store visits.
- Journey Stages: Different stages a customer goes through, such as awareness, consideration, decision, purchase, and post-purchase.
- Emotional States: Understanding the emotions and attitudes of customers at each stage of their journey.
- Pain Points and Challenges: Identifying obstacles and frustrations customers encounter throughout their journey.
- Opportunities for Improvement: Areas where the brand can enhance customer experience and engagement.
Path to Purchase Mapping
Path to Purchase Mapping specifically focuses on the stages and touchpoints involved in a customer’s decision-making process leading to a purchase. It provides a detailed visualization of how customers move from initial awareness of a product or service to the final purchase decision. Key elements include:
- Awareness: The stage where customers first become aware of a product or service through advertising, word-of-mouth, social media, etc.
- Consideration: The stage where customers actively seek information, compare options, read reviews, and evaluate the product’s benefits.
- Intent: The stage where customers show a clear intent to purchase, such as adding items to a cart, signing up for newsletters, or engaging with sales representatives.
- Purchase: The stage where customers complete the transaction, making the actual purchase.
- Post-Purchase: The stage where customers use the product, share feedback, seek customer service, and engage in repeat purchases or advocacy.
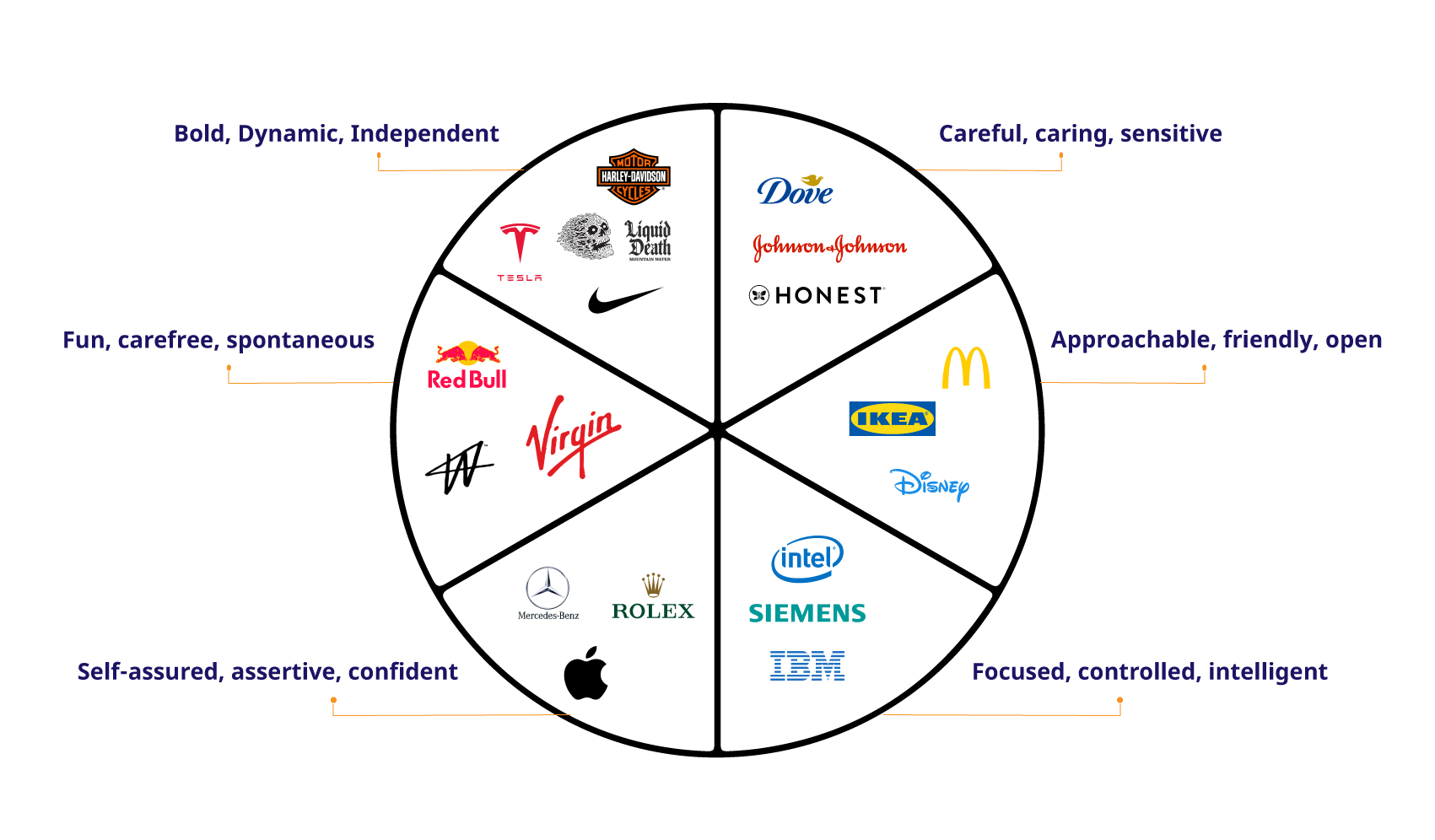
Continue reading: What is a Brand Wheel and How is it Used?
Steps to Create Consumer and Path to Purchase Maps
- Research and Data Collection:
There are a lot of ways you can gather data such as from customer surveys, interviews, focus groups, and analytics. You can use tools such as Google Analytics, CRM systems, social media insights, and customer feedback platforms.
We like to use Valuegraphics data, which is a comprehensive database of consumer values turned into data. Rather than relying on demographics and psychographics, which are fleeting and limited, valuegraphics understands what a person values and therefore how they are likely to behave.
NOTE: If you’d like to learn more about how to obtain valuegraphics data, please contact us.
2. Identify Customer Personas:
The way traditional customer profiles have been created are fatally flawed and utterly useless. They are based on demographic and psychographic data (please see point 1 where I talk about the value of valuegraphics.)
Nevertheless, you still need to identify your different customer segments.
While you can include demographic information, behaviour patterns, preferences, and pain points, you will should use valuegraphics.
3. Map Out Touchpoints:
Next, you’ll want to identify all points of interaction between the customer and your brand.
A customer touchpoint is any interaction or point of contact between a business and its customers or potential customers throughout their journey with the brand. These interactions can occur before, during, or after a purchase and can happen in various physical or digital environments. Understanding and optimizing touchpoints are crucial for creating a seamless and positive customer experience, fostering loyalty, and driving sales.
Continue reading: Understanding Customer Touchpoints
4. Define Journey Stages:
Break down the customer journey into distinct stages.
Assign specific touchpoints and actions to each stage.
A typical customer journey can be broken down into several distinct stages. These stages represent the different phases a customer goes through from the moment they become aware of a brand to post-purchase engagement. The exact stages may vary depending on the business and industry, but a common framework includes:
Awareness:
- Objective: Make potential customers aware of your brand or product.
- Touchpoints: Social media posts, online ads, blog articles, influencer marketing, PR campaigns, search engine results, website content.
- Actions: Create engaging content, launch advertising campaigns, optimize SEO, collaborate with influencers, and participate in events or sponsorships.
Consideration:
- Objective: Help potential customers evaluate your product or service.
- Touchpoints: Product pages, comparison charts, customer reviews, testimonials, email newsletters, webinars, live chats.
- Actions: Provide detailed product information, create comparison guides, share customer testimonials and case studies, offer free trials or demos, and host informative webinars.
Decision:
- Objective: Encourage potential customers to make a purchase decision.
- Touchpoints: Pricing pages, shopping cart, checkout process, customer service, promotional offers, retargeting ads.
- Actions: Simplify the checkout process, offer limited-time promotions, provide clear and transparent pricing, ensure customer support availability, and use retargeting ads to remind customers of their interest.
Purchase:
- Objective: Facilitate a smooth and satisfactory purchasing experience.
- Touchpoints: Order confirmation emails, payment gateways, shipping notifications, thank-you pages.
- Actions: Send order confirmation and shipping updates, ensure a secure and easy payment process, offer customer support for any purchase-related issues, and include a thank-you message.
Post-Purchase:
- Objective: Build loyalty and encourage repeat purchases.
- Touchpoints: Follow-up emails, customer surveys, loyalty programs, customer support, social media engagement, product tutorials.
- Actions: Send follow-up emails thanking customers and asking for feedback, offer loyalty rewards or discounts, provide excellent customer support, engage with customers on social media, and create tutorials to help them get the most out of their purchase.
Advocacy:
- Objective: Turn satisfied customers into brand advocates.
- Touchpoints: Referral programs, social media interactions, user-generated content, community forums, customer testimonials.
- Actions: Launch referral programs with incentives, encourage customers to share their experiences on social media, showcase user-generated content, create community forums for discussions, and feature customer testimonials on your website and marketing materials.
5. Analyze Emotional States and Pain Points:
Understand the emotions and challenges customers face at each stage. You can pull in customer feedback to identify pain points.
We talk about two frameworks that could be useful here:
6. Implement and Iterate:
Use the insights gained from mapping to inform marketing strategies, product development, and customer service improvements. After your campaigns and strategies have been implemented, you’ll want to continuously monitor and update your strategy based on new data and customer feedback.
If you identify any areas where the customer experience can be enhanced, then you can further refine or develop your strategies to optimize your approach to address pain points and improve engagement.
Continue reading:
If You’re Not Disrupting, You’re Standing Still
- Related post: The T-Shirt Theory of Branding
- Related post: The Power of Branding: John’s Family Premium Organic Garlic
- Related post: Why You Don’t Want to Run a Business that Relies Solely on Ads


Continue reading: What’s the ROI of a Billboard
Related Posts
Need help with your marketing activities?
If you’re looking to make a move with your marketing, reach out to us. We are priced fairly, we’re straight shooters, and are the very best at what we do.